Understanding Terpenes: What is Terpinolene?

- 1. What is terpinolene?
- 2. Where can you find terpinolene?
- 3. What are terpinolene's uses?
- 3. a. Terpinolene as a natural antiseptic
- 3. b. Terpinolene to fight fungi and bacteria
- 3. c. Terpinolene for sleep and its relation to cbn
- 3. d. Terpinolene and its relation to cancer
- 3. e. Terpinolene for heart disease and antioxidation
- 4. What are some terpinolene rich strains?
- 5. The bottom line
If you're reading this, the odds are you are one of those stoners who taste cannabis as if you were in a wine tasting, of course perhaps you're just randomly wandering around the blog, those who carefully choose each strain on foundation-based decisions.
For this, it's essential to understand what makes the characteristics of a cannabis plant, how tall it will be, whether it is a Sativa, Indica, or Hybrid, what's the THC and CBD content, and one of the most commonly researched characteristic, the taste and aroma of each strain.
Now, when it comes to taste and aroma, what you should be looking for is what's known as terpenes. In nature, most plants and fruits are full of fragrant oils, cough-cough, terpenes, which are the components that give each of these their own characteristic scent and taste.

In the world of cannabis, there is a wide variety of terpenes that not only characterize each strain's flavor and aroma but they provide several health properties, according to their combination with other terpenes and cannabinoids as well.
For instance, if you ever sensed woody, floral, herbal, or piney hues of flavor while you enjoyed some cannabis buds, then you most likely got the hold of some terpinolene-rich weed buds.
Let's find out what terpinolene is and what are its properties.
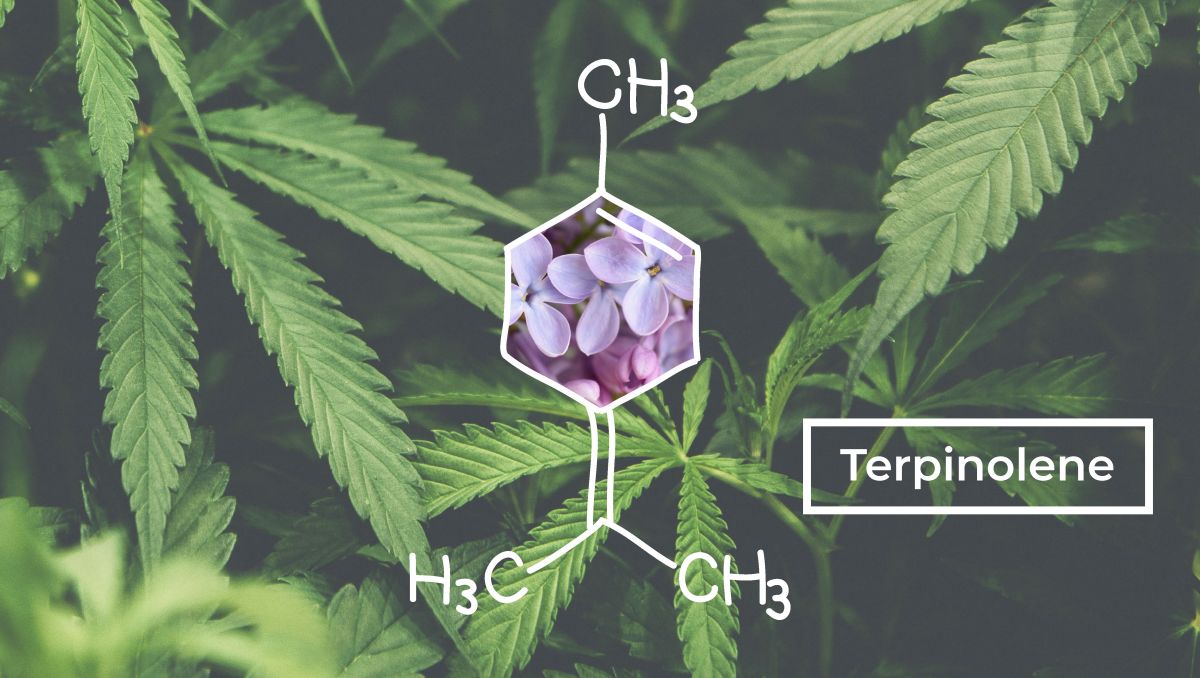
1. What Is Terpinolene?
Terpinolene (ter-pin-uh-leen), is considered one of the least common terpenes in the cannabis terpenes family. As we mentioned above, it is that one characteristic of floral, woody, and even slightly fruity hues of smell and taste.
Just like many of the other terpenes, terpinolene has emerged as a defense mechanism for plants, which use these strong scents and flavors to disguise and repel pests and insects from attacking them.
Terpinolene, as well as most of the other terpenes, are secreted in marijuana plants' trichomes, the shiny mushroom-looking glands where other cannabinoids are produced as well, such as the famous CBD and THC.
These fragrant oils, which aren't psychoactive by themselves, aren't only the ones to determine the smell of plants and herbs but they also come along with several health benefits and properties.
2. Where Can You Find Terpinolene?
Apart from being present in cannabis plants and buds, terpinolene terpenes can also be found in several products from nature. Terpinolene is also commonly found in apples, rosemary, sage, nutmeg, cumin, lilacs, conifer trees, and tea trees.
When it comes to cannabis, terpinolene is usually present in strains that aren't too rich in CBD but in THC. The main reason for this is simply because marijuana breeders still need to address the research of the terpene contents in CBD-dominant strains. For the moment, CBD strains rich in terpinolene content are still uncommon to find, but they could definitely be created by master breeders.
When it comes to the type of marijuana strains, terpinolene terpenes tend to be more predominant in Sativa cannabis strains, although they can be found in Indicas as well.
3. What Are Terpinolene's Uses?
Since terpinolene's distinctive smell is usually described as 'fresh', you will be able to find plenty of these terpenes as an additive to plenty of products in the cleaning and cosmetics section, such as soap, perfumes, and air fragrances.
Another common use for terpinolene terpenes is for insecticides and insects repellent. Terpinolene shares this attribute with two other famous terpenes in the cannabis family, limonene and pinene.
Terpinolene can also be employed for the making of plastics and resin, as well as for flavoring food and beverages. At the same time, this fragrant oil provides several health benefits as well, such as:
- Decreasing the risks of heart disease;
- Working as a natural antiseptic;
- Inhibiting the growth of certain cancer cells;
- Working as an antifungal and antibacterial;
- Providing sedative effects to aid sleep;
- Being an antioxidant, and more.
Let's go through the properties of terpinolene terpenes in detail.
Terpinolene as a Natural Antiseptic
Unlike the other terpenes, terpinolene doesn't provide any internal anti-inflammatory or pain-relieving properties to the body, but it does work as a natural antiseptic.

This component has been used for thousands of years as a natural alternative to treat open wounds, aiding to keep it clean from germs and infections, and working externally to decrease inflammation and relieve pain.
Terpinolene to Fight Fungi and Bacteria
One of the main qualities of terpinolene resides in its capacity to act as an anti-bacterial, anti-microbial, and antifungal. Hence its presence in tea tree oil, which has been anciently used as a traditional form of medicine, it is no surprise to hear that terpinolene is an effective component to fight bacteria and fungi growth and propagation.
A study led in the year 2015 came to confirm this property in terpinolene terpenes. The research was based on a type of Diplotaenia damavandica plant, a variety that has a 20% terpinolene content in its genetic composition.
The study's results showed that this terpene is indeed efficient in the prevention of E. coli bacteria, Salmonella, and other common bacteria and fungi. 1

Furthermore, as we already know, terpinolene originated to fulfill the plants' needs to shelter from predators in their natural habitats. Therefore, a study led in 2009 backs up this by having found that this terpene, as well as many others, is in fact an essential component in pesticides, aiding to get rid of mosquitoes, beetles, and weevils.
Terpinolene for Sleep and Its Relation to CBN
CBN, or cannabinol, is one of the ten most famous cannabinoids present in cannabis plants. This is the one known for providing deep sedative effects, being often referred to as the sleepy cannabinoid.
Terpinolene, for its part, is also a great sedative compound in the cannabis family tree, not only because it works as an enhancer of CBN cannabinoids, but because it has these properties on its own too.
In 2013, researchers who performed studies on rats were set on demonstrating this property of terpinolene terpenes, which they achieved successfully. The rodents in the study, were induced into sleep once they were exposed to the inhalation of these compound.2
Therefore, it is safe to say that terpinolene-rich cannabis strains could aid those who are struggling with sleep and help relieve anxiety and stress as well.
Terpinolene and Its Relation to Cancer
A study published in 2012 in the journal Oncology Letters affirmed that terpinolene is a potent anti-cancer component. Said study reported that this terpene notoriously decreased the protein expression levels of a protein that is known for enhancing cancer cell spread.3
The research used not cannabis but rosemary and sage extracts, both natural treatments that are rich in terpinolene levels. Not only does this back the anti-cancer quality of these compounds, but its malignant cell inhibitor capacity.
Terpinolene for Heart Disease and Antioxidation
Living in a world where all everyone really wants is to stay young forever, we're always on the hunt for antioxidant sources. Antioxidants are compounds that act against oxidation, which is what causes the human body to age.

Like many of the other terpenes, terpinolene has shown to aid successfully in inhibiting the process of oxidation. This is backed up by a study led in 2005, which found that terpinolene reduces LDL, low-density lipoproteins oxidation, which is also known as 'bad cholesterol'.4
By inhibiting LDL and bad cholesterol, these terpenes, in turn, reduce cell damage and decrease the risks of heart disease as well, which is strongly linked to these phenomena.
5. What Are Some Terpinolene Rich Strains?
Now that we've successfully gone through the variety of benefits you can get from terpinolene terpenes, we hope we've served you as a guide to identify which compounds you should seek for in your cannabis plants and buds.
If terpinolene is exactly the compound you crave, then definitely check out our Orange Sherbet Auto strain. This 24% THC content beast is a heavyweight Sativa, with a 70-30 balance, ideal for those who enjoy feeling euphoric.
If you're more of a pineapple fan, then Pineapple Express Auto might just be your strain. We've created this one inspired by the famous movie starring Seth Rogen and James Franco. Rich in pineapple flavors, Pineapple Express is a more balanced hybrid strain.
6. The Bottom Line
There's more to the world of cannabis consumption than just pulling out a grinder, rolling one, and getting high. The same goes for cultivation, it's not just about throwing some seeds on the ground and watering them.
Of course, you could indeed keep that state of mind, but you would be missing on so much. Cannabis is a complex plant, and the more you investigate and read about it, the more you'll improve your consumption experience.
By identifying your favorite terpenes and their effects, you'll be able to indulge your own personal taste's favorite strains and make the most out of these plants' fruits.
EXTERNAL REFERENCES
- "Essential oil composition and antimicrobial activity of Diplotaenia damavandica" Fereshteh Eftekhar, Morteza Yousefzadi, Dina Azizian, Ali Sonboli, and Peyman Salehi. November-December 2005.
- "The sedative effect of inhaled terpinolene in mice and its structure-activity relationships." Ito K. and Ito M. January 2013.
- "Terpinolene, a component of herbal sage, downregulates AKT1 expression in K562 cells" Naoko Okumura, Hitomi Yoshida, Yuri Nishimura, Yasuko Kitagishi, and Satoru Matsuda. February 2012.
- "The monoterpene terpinolene from the oil of Pinus mugo L. in concert with alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene effectively prevents oxidation of LDL" J. Grassmann, S. Hippeli, R. Spitzenberger, and E.F. Elstner. June 2005.













Comments