What Are Flavonoids in Cannabis?

- 1. What are flavonoids?
- 2. Most common flavonoids
- 2. a. Flavonols
- 2. b. Flavanones
- 2. c. Anthocyanins
- 2. d. Isoflavonoids
- 2. e. Other flavonoids
- 3. Cannflavins
- 4. Flavonoids and the entourage effect
- 5. Maximizing the benefits of flavonoids
- 6. In conclusion
Feminized seed plants produce hundreds of different chemical compounds, such as cannabinoids and terpenes. Both cannabinoids and terpenes are responsible for the type of high you experience when consuming cannabis but recent research discovered a new type of chemical compound that’s also believed to affect the type of high. Flavonoids are chemical compounds responsible for a cannabis plant's flavor while also playing a major role in the distinctive color cannabis plants can have.
1. What Are Flavonoids?
Flavonoids are part of a larger group of chemical compounds called polyphenols and are found in plants, fruits, and vegetables. Have in mind that not all polyphenols are flavonoids, despite their similarities, there are approximately 4000 different flavonoids out of a total of 8000 polyphenols, meaning that all flavonoids are polyphenols but not all polyphenols are flavonoids. As mentioned, flavonoids are found in most plants and are responsible for the different colors, smells, and flavors plants have while also being important in plant protection and reproduction. This happens because some flavonoids emit a strong odor that keeps away bugs and other flavonoids emit an odor that certain pollinators seek after, thus helping in reproduction and spreading seeds.
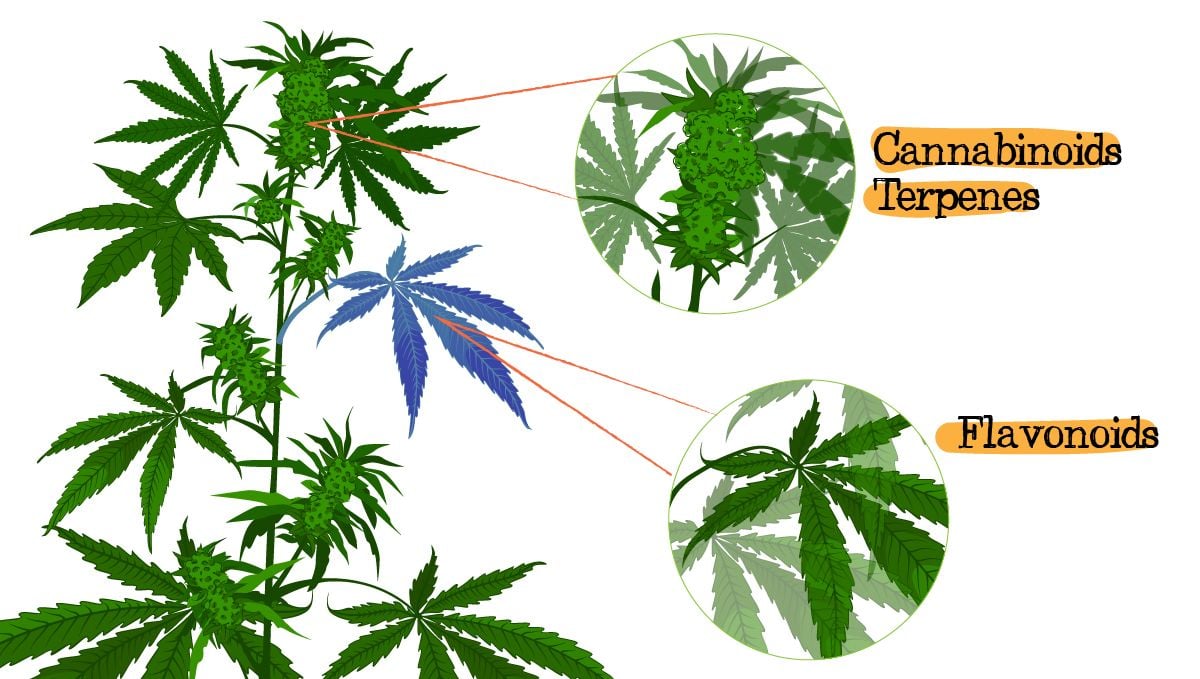
Flavonoids also influence the aroma and flavor of cannabis but, unlike terpenes and cannabinoids, flavonoids are present in other parts of the cannabis plant, such as stems, leaves, and seeds, so despite being usually disposed of, the leaves can be used to make super healthy smoothies. Apart from being beneficial for plants, flavonoids are also beneficial for humans. As it turns out, just like terpenes, flavonoids have anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. There’s no concrete data to confirm it but scientists say that a clear indication is the lower incidence of chronic diseases such as coronary heart disease, hypertension, and stroke in regions where people consume a lot of fruits and vegetables, such as the Mediterranean region.
2. Most Common Flavonoids
Despite terpenes being better known in the cannabis world, flavonoids are actually found in higher concentrations than terpenes. Scientists have already found over 20 different flavonoids in cannabis, basically divided into three main groups:
- Flavonols;
- Flavanons;
- Isoflavonoids and;
- Anthocyanins among others.
Flavonols
Flavonols are a group of flavonoids that includes kaempferol and quercetin, both of these chemicals have antioxidant properties and can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Ongoing studies are currently assessing this class of chemical compounds for potential health benefits. So far, researchers have probed them in specific models that have assessed anti-inflammatory and cancer-preventative activities. More specifically, studies looking at the flavonol kaempferol found that the molecule might help to reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer—one of the deadliest forms of cancer.
On top of this, additional research suggests that quercetin possesses anti-inflammatory effects that could help to curb the symptoms of several conditions, including asthma and arthritis. Considering inflammation plays a pivotal role in many states of modern chronic disease, intaking flavonols through cannabis and other dietary avenues could help to soothe our bodies and keep us healthy for longer.
Flavonols
| Also Found in: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Onions | Lettuce | Berries | Grapes |
| Kale | Tomatoes | Apples | Tea |
Flavanones
Flavanones also have antioxidant properties but the main benefit is they help get rid of molecules that can damage your cells, potentially protecting you against cancer and several diseases. This flavonoid can also reduce cholesterol and offers anti-inflammatory properties.
Flavanones
| Also Found in: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mandarins | Oranges | Kumquat | Grapes |
| Lemons | Lime | Clementine | Grapefruit |
If you’re looking for a strain that offers all the health benefits flavanones do, make sure to take a look at our incredibly citrus Orange Sherbet Auto!
Flavanones are mainly found in citrus fruits because they’re one of the compounds that give citrus fruits the bitter flavor.
Anthocyanins
This flavonoid is believed to have both anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, and it’s mostly found in the following foods:
Anthocyanins
| Also Found in: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Blackcurrants | Cabbage | Strawberries | Cranberries |
| Eggplant | Blueberries | Cherries | Blackberries |
Anthocyanins are probably the most popular flavonoid because it gives plants, fruits, and vegetables their distinctive blue, purple or red colors. Striking colors aside, these pigments also play an important role in plant biology. By reflecting specific wavelengths of light, they serve as a natural plant sunscreen that protects tissues from the detrimental effects of UV radiation. Furthermore, they also help to regulate plant growth and also work as antioxidants to protect cells against free radical damage. Outside of plants, anthocyanins also form an important part of the human diet. Ongoing studies suggest that they possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that protect our cells from oxidation that’s linked to DNA damage and a host of diseases, including cancer. These colorful molecules are also linked to improving cognitive function and may play an important role in maintaining brain health and function as we age.
Isoflavonoids
Isoflavonoids play a role in metabolism and hormonal balance because they have phytoestrogenic effects that mimic estrogen. Meaning that isoflavonoids could benefit pre and post-menopausal women in combating conditions and symptoms caused by estrogen deficiency. During menopause, levels of estrogen naturally decrease. This shift in hormones gives rise to a number of symptoms that can affect a woman's quality of life, including reduced bone density, mood swings, and hot flashes. Isoflavonoids might help to manage these symptoms in some women by acting as a plant-derived estrogen substitute. Because this compound works in a similar way in the body, it could help to reduce the severity of menopause symptoms. You can think about it in the same way as THC and other cannabinoids mimicking the natural endocannabinoids found in the body.
Isoflavonoids
| Also Found in: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Soybeans | Raisins | Lentils | Fava beans |
| Chickpeas | Pistachios | Peanuts | Potatoes |
Other Flavonoids
As mentioned before, scientists believe there are over 4000 flavonoids but we still don’t know all of them and we know very little about the ones we know. Anthocyanins, Flavonols, Flavanones and Isoflavonoids are the main flavonoids known but there are other flavonoids that even though we know they exist and where they exist, we don’t know much about them, they are:
- Catechins and;
- Chalcones.
These flavonoids are found in bananas, apples, pears, and peaches among other fruits, and offer antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidative properties but more research is needed in order to understand catechins, chalcones, and all other flavonoids better.
3. Cannflavins
Apart from the flavonoids mentioned in this blog article, there are some flavonoids exclusive to cannabis plants. They are Cannflavin-A, Cannflavin-B, and Cannflavin-C. Cannflavins were first identified in 1986 when researchers found their anti-inflammatory properties to be thirty times stronger than aspiring A couple of years ago researchers figured out how cannflavins are made in the cannabis plant and according to a study published in 2020, claimed that cannflavins could even treat pancreatic cancer but these findings are just the tip of the iceberg.
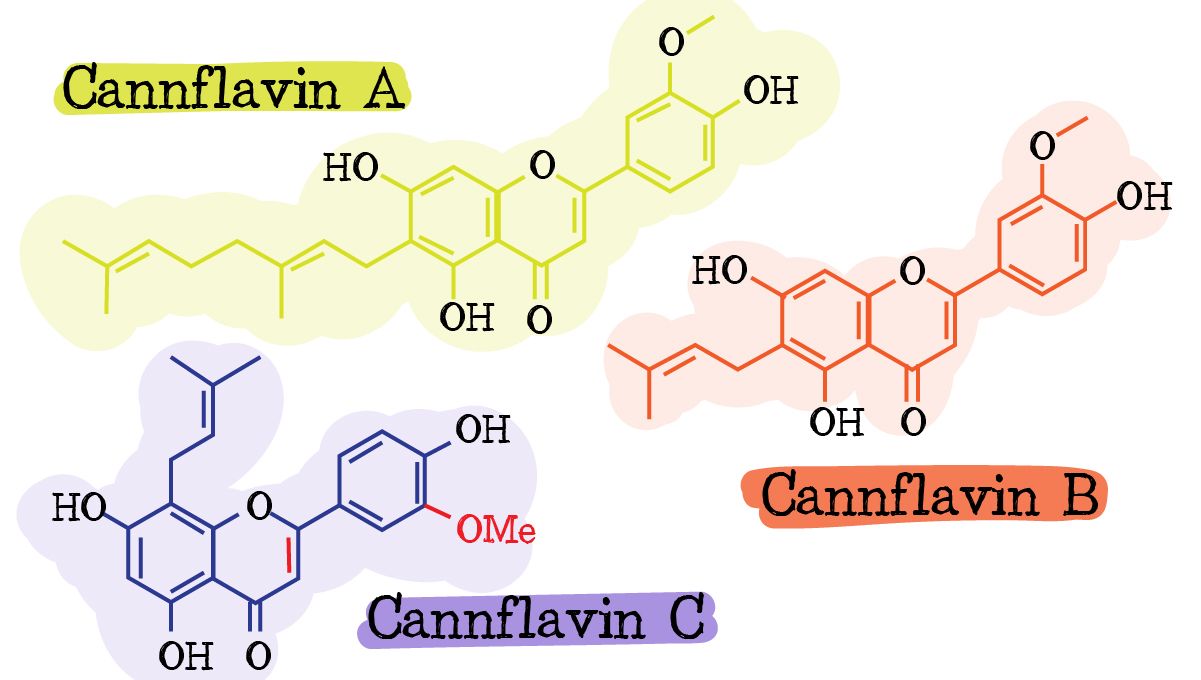
Unfortunately, cannabis prohibition made it hard for researchers to learn more about cannflavins because even though cannflavins aren’t illegal cannabis plants are. And not long ago, possessing, growing, and using cannabis was still illegal, which made it impossible for scientists to research cannabis-exclusive flavonoids. This means that despite knowing their benefits, we still need to know much, much more in order to understand how to make the most out of all the beneficial chemical compounds such as cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids produced by cannabis plants.
4. Flavonoids And the Entourage Effect
Flavonoids possibly play a role in the entourage effect due to being partially responsible for the flavor and aroma of cannabis plants. For those who don’t know what the entourage effect is, it refers to how the different cannabis compounds such as cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids work together to provide a more complete effect. This happens because flavonoids help increase the bioavailability of cannabinoids in the body, also influence how the cannabinoids are transported in your body and how they interact with the cannabinoid receptors.
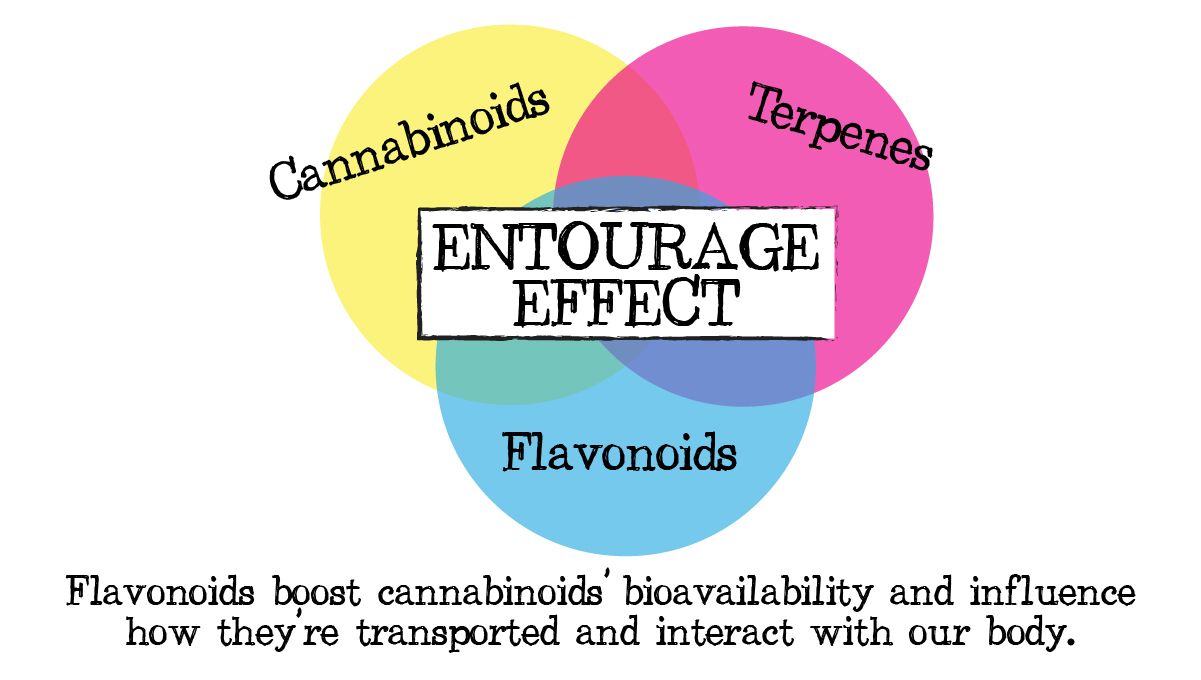
On top of that, researchers believe flavonoids can affect a specific enzyme that is involved in metabolizing THC and CBD. All of these reasons are why you should always opt for full-spectrum concentrates rather than isolates.
5. Maximizing the Benefits of Flavonoids
Flavonoids are found in cannabis and other plants and fruits, and they're extremely important as they’re responsible for the pigmentation of flowers and fruits but also help plants attract pollinators and fight against bugs. There’s still not much information on the direct effects of flavonoids but it’s thought that flavonoids work together with cannabinoids and terpenes, boosting their effectiveness. If you’re interested in maximizing the benefits that flavonoids have to offer, you should opt for the consumption method that delivers the most. And despite not being 100% confirmed as there’s not much research on flavonoids, researchers believe that the best way to maximize flavonoid consumption would be by eating cannabis flowers…but why?
Well, smoking a joint or taking a bong hit, for example, exposes flavonoids to fire which can activate certain flavonoids but will burn up others. This means that the best way to maximize flavonoids is to NOT expose them to heat but edibles, oils, and tinctures can also be a great way to consume flavonoids, depending on how you decarboxylate your flowers as it’s recommended to go for lower temperatures. Remember that temperatures over 70 to 75 °C can destroy them so always try to stay below that. There’s still a lot more we need to know about flavonoids, their benefits, and the best way to maximize flavonoid production, but as you may know, cannabis is still illegal in most places so is difficult to conduct research.
6. In Conclusion
Flavonoids are found in most plants, including cannabis, and have a lot of health benefits that can protect you against several conditions. But, most of the flavonoids are in the cannabis plant’s leaves and branches so in order to get these benefits you should consume them.
A great way to consume cannabis flavonoids is to mix the leaves in foods and drinks, such as salads and smoothies; So if you are wondering how to consume cannabis flavonoids, you can use the big fan leaves to make super nutritious smoothies.
If you know any tips to help fellow growers consume cannabis flavonoids, feel free to share them in the comment section below!
External References
- Cannflavins - From plant to patient: A scoping review - Simon Erridge, Nagina Mangal, Oliver Salazar, Barbara Pacchetti and Mikael H Sodergren.
- The Hallmarks of Flavonoids in Cancer. Molecules. - Ponte, Luis & Pavan, Isadora & Mancini, Mariana & Silva, Luiz & Morelli, Ana & Severino, Matheus & Bezerra, Rosangela & Simabuco, Fernando. (2021).
- Flavonoids in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. - Rao, Prashant & Mainkar, Ojas & Bansal, Nitin & Rakesh, Neal & Haffey, Paul & Urits, Ivan & Orhurhu, Vwaire & Kaye, Alan & Urman, Richard & Gulati, Amitabh & Jones, Mark. (2021).













Comments